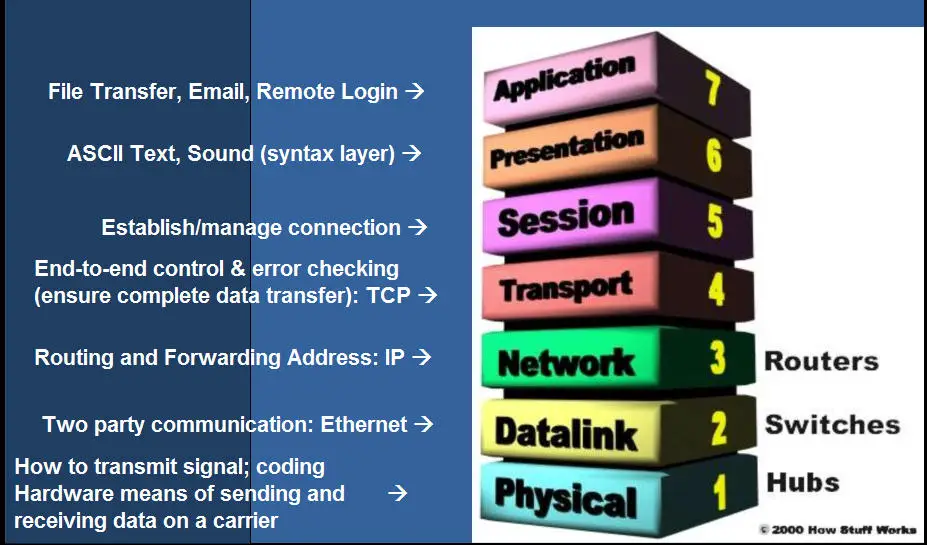
Open Systems Interconnection model describes the hypothetical architecture for networks and provides a framework into which other standards and products should fit in.
OSI model is based on layered architecture where each layer plays a vital role in the overall communication effort and interacts with the other layers above and below it and also with the corresponding layer in the other network. It consists of seven layers namely from bottom to top; Physical Layer, Data Link Layer, Network Layer, Transport Layer, Session Layer, Presentation Layer and application Layer.
Suppose we have an application running on computer A producing some data to be transmitted to computer B then the flow of data transmission will be from Application layer of computer A to the Physical Layer of Computer A, along the physical network and then from Physical Layer of B to the Application Layer of B. Each layer does the following:
Physical Layer: This is non software layer and deals with physical connection between the network nodes.
Data Link Layer: This layer is responsible for the transmission of data packets
Network Layer: This layer is responsible for the routing of data packets
Transport Layer: This layers controls the correct delivery of packets and resends the packets in case of lost
Session Layer: This layer maintains the logical session between the two nodes
Presentation Layer: This layer resolves any data encoding between communicating nodes
Application Layer: This layers present data in full form to the user as delivered from sending node to the receiving node
OSI model is based on layered architecture where each layer plays a vital role in the overall communication effort and interacts with the other layers above and below it and also with the corresponding layer in the other network. It consists of seven layers namely from bottom to top; Physical Layer, Data Link Layer, Network Layer, Transport Layer, Session Layer, Presentation Layer and application Layer.
Suppose we have an application running on computer A producing some data to be transmitted to computer B then the flow of data transmission will be from Application layer of computer A to the Physical Layer of Computer A, along the physical network and then from Physical Layer of B to the Application Layer of B. Each layer does the following:
Physical Layer: This is non software layer and deals with physical connection between the network nodes.
Data Link Layer: This layer is responsible for the transmission of data packets
Network Layer: This layer is responsible for the routing of data packets
Transport Layer: This layers controls the correct delivery of packets and resends the packets in case of lost
Session Layer: This layer maintains the logical session between the two nodes
Presentation Layer: This layer resolves any data encoding between communicating nodes
Application Layer: This layers present data in full form to the user as delivered from sending node to the receiving node